Sound Absorption and Reverberation Times
Eu absorption classification (EN ISO 11654)
Sound absorption coefficients are measured according to ISO 354. The weighted sound absorption coefficient (αw) and the sound absorption class as shown in the table below have been calculated according to ISO 11654.
| Absorption class | Weighted absorption coefficient | Description |
| A | αw 0,90 – 1,00 | Extremely absorbing |
| B | αw 0,90 – 0,85 | Extremely absorbing |
| C | αw 0,60 – 0,75 | Highly absorbing |
| D | αw 0,30 – 0,55 | Absorbing |
| E | αw 0,15 – 0,25 | Hardly absorbing |
| No Class | αw 0,00 – 0,10 | Reflecting |
US noice reduction coeficients (ASTM 423)
NRC (Noice Reduction Coefficient) is determined as a value that comes from the average value achieved on the following frequencies: 250, 500, 1000 and 2000 Hz. Approximate translation from αw to NRC:
| αw | NRC |
| A | NRC > 0,75 |
| B | NRC > 0,75 |
| C | 0,5 < NRC < 0,75 |
| D | 0,5 < NRC < 0,75 |
| E | 0,25 < NRC < 0,5 |
| No Class | NRC < 0,25 |
Please note that using sound absorbing materials with for example class B not automatically results in a room with class B, the whole room could actually be classified higher or lower.
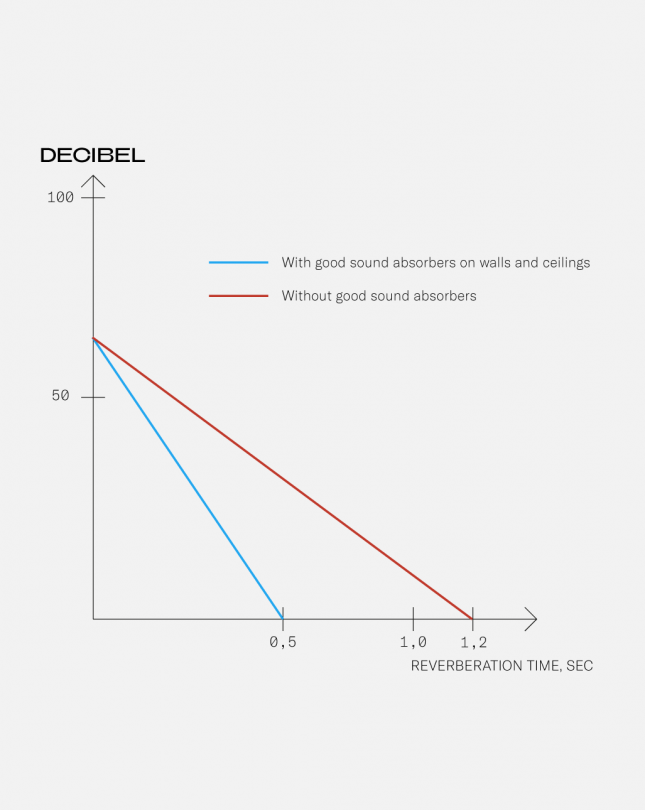
3 factors affecting reverberation time
1. The volume of the room. A larger room means a longer reverberation.
2. The surfaces of the room. More absorbing surfaces gives a shorter reverberation.
3. The objects in the room. More objects result in a shorter reverberation.
The total sound absorbing effect of the surface materials in a room is the result of how well the material absorbs sound, multiplied by the total area of the walls and ceilings covered. Gustafs provides wall and ceiling solutions with very good sound absorbing qualities and they can cover large surfaces of the room, the ideal combination.
